In this article you will see how you can use gulp to automate several tasks that you usually do by hand or for which you rely on tools developed by others.
What Is Gulp
Gulp is a streaming build system. You might have heard about and used grunt already. But lately gulp is getting more popular. It can do amazing stuff like compiling LESS/Sass, JS files, live reloading web pages and lots more.
Why Use Gulp
It can save you a lot of time by automating several tasks. And the best thing is you have the power to tell it what to do, unlike relying on third party tools to implement certain functionality. In short you can build your own automation tool as per your set of needs.
Prerequisites
In order to get started you need to have Node.js (v0.10.30 or higher) installed. I personally prefer to use Node Version Manager (NVM) so that I can switch between different versions of Node.js on my development machine.
Let's Get Started
The first thing you need to do is install gulp. Use the following command from terminal to do so.
npm install -g gulp
This will install gulp globally on your machine.
Let's start setting up the automation tool by creating a directory in the WordPress themes folder or any preferred location you want.
In my case I will navigate to the themes folder...
cd ..../wp-content/themes
... and run the following command.
mkdir wp-gulp-automation
Now I will navigate to the folder to initiate a npm project.
cd wp-gulp-automation npm init
This will ask you several questions like project name, version, description, author, license, etc.
You may either fill them in or keep hitting Enter until it says yes. Lastly type yes and hit Enter one more time.
This will create a package.json file in the directory. It holds information about your project and its dependencies.
If you have followed the process correctly, your package.json file will look like this:
{
"name": "wp-gulp-automation",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
First Gulp File
Install gulp locally to your project.
npm install gulp --save-dev
This will create a node_modules folder and keep all your project dependencies in there. --save-dev is used to update dev-dependencies in package.json.
Create gulpfile.js in the project directory with the following code.
var gulp = require('gulp');
gulp.task('default', function(){
console.log('default gulp task...')
});
In the terminal type gulp and hit Enter. You will see the above text is logged to the console.
Creating a Basic Sass Compilation Tool
There are various gulp plugins available for Sass compilation. I have tried and listed three of them below.
- gulp-sass (simple and easy to use)
- gulp-compass (works great with compass-based projects)
- gulp-ruby-compass (this one gives more control than the other two)
For the sake of simplicity, in this tutorial I will use the first one, that is gulp-sass.
Run the following command in the project directory to install it.
npm install gulp-sass --save-dev
Lets update the code to compile Sass files into CSS files.
Add require at the top of gulpfile.
var sass = require('gulp-sass');
gulp.task('sass', function () {
gulp.src('./css/src/*.scss')
.pipe(sass())
.pipe(gulp.dest('./css'));
});
gulp.task('default', ['sass']);
Now when I run gulp sass in terminal, the sass task is fired.
And because I have added it to an array of default tasks, when I run gulp in terminal, the default task fires the sass task.
What this will do is compile all the files in the css/src folder of the project and save them to the css folder. You may want to pass extra options to the sass() function depending on your needs.
So basically running gulp and gulp sass will do the same thing at this time.
Lint and Compile JS Files
Next, in order to have better and packaged JavaScript code in your themes, you need gulp-jshint and gulp-concat.
npm install gulp-jshint --save-dev npm install gulp-concat --save-dev
Now add require at the top of gulpfile:
var jshint = require('gulp-jshint');
var concat = require('gulp-concat');
Add the following gulp task to the file to lint and combine all js files.
gulp.task('js', function () {
gulp.src('js/src/*.js')
.pipe(jshint())
.pipe(jshint.reporter('fail'))
.pipe(concat('theme.js'))
.pipe(gulp.dest('js'));
});
If you want to organize a little more, you can have vendor and theme folders inside js/src. The vendor folder contains all the third-party libraries such as jQuery plugins, and the theme folder will contain your own theme's JavaScript code.
If you want to minify them too, you can include the gulp-uglify plugin. And let's update our default task to:
gulp.task('default', ['sass', 'js']);
Optimize Images
The most commonly used gulp plugin for this task is gulp-imagemin. Install it by using:
npm install gulp-imagemin --sav-dev
Add require gulp-imagemin at the top:
var imagemin = require('gulp-imagemin');
And add the following task to the gulpfile.
gulp.task('img', function() {
gulp.src('img/src/*.{png,jpg,gif}')
.pipe(imagemin({
optimizationLevel: 7,
progressive: true
}))
.pipe(gulp.dest('img'))
});
What this will do is make an optimized copy of all the images placed in the img/src directory into the img directory.
Add it to the default tasks list.
gulp.task('default', ['sass', 'js', 'img']);
Watch Task
Next is setting up a watch for automating tasks.
gulp.task('watch', function() {
gulp.watch('css/src/*.scss', ['sass']);
gulp.watch('js/src/*.js', ['js']);
gulp.watch('img/src/*.{png,jpg,gif}', ['img']);
});
Adding it to the default tasks list gives us:
gulp.task('default', ['sass', 'js', 'img', 'watch']);
Error Handling
What happens if an error occurs while running one of our tasks? Your gulpfile will stop running.
In order to handle that, let's use a nice gulp plugin called gulp-plumber. We'll also use gulp-notify to show nice growl life notifications upon errors.
Install gulp-plumber and gulp-notify using:
npm install gulp-plumber --save-dev npm install gulp-notify --save-dev
Again require this at the top of gulpfile.
var plumber = require('gulp-plumber');
var notify = require('gulp-notify');
Here is a handy plumber setting that I will use when an error occurs in any of the tasks.
var plumberErrorHandler = { errorHandler: notify.onError({
title: 'Gulp',
message: 'Error: <%= error.message %>'
})
};
Now our updated sass task will look like:
gulp.task('sass', function () {
gulp.src('./css/src/*.scss')
.pipe(plumber(plumberErrorHandler))
.pipe(sass())
.pipe(gulp.dest('./css'))
});
Notice the plumberErrorHandler added. In the same way I will add this to the js and img tasks.
Live Reload
One important thing needed is live reload functionality.
First of all install a browser extension/addon for live reload:
Now you need to install gulp-livereload using:
npm install gulp-liveraload --save-dev
One more time add it to the top where you require in gulpfile.
var livereload = require('gulp-livereload');
Lets update our tasks to include live reload now.
The sass task will look like this:
gulp.task('sass', function () {
gulp.src('./css/src/*.scss')
.pipe(plumber(plumberErrorHandler))
.pipe(sass())
.pipe(gulp.dest('./css'))
.pipe(livereload());
});
Similarly add livereload to the js and img tasks. One more thing you need to do is add livereload.listen(); at the beginning of the watch task.
gulp.task('watch', function() {
livereload.listen();
gulp.watch('css/src/*.scss', ['sass']);
gulp.watch('js/src/*.js', ['js']);
gulp.watch('img/src/*.{png,jpg,gif}', ['img']);
});
In order to test livereload, let's create an index.php file with the following code.
<html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="<?php echo get_template_directory_uri(); ?>/css/style.css"> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1>hello from gulp automation tool</h1> <script type="text/javascript" src="<?php echo get_template_directory_uri(); ?>/js/theme.js"></script> </body> </html>
And a style.css.
/* Theme Name: Tutsplus gulp wp automation Theme URI: http://tutsplus.com Description: Automating wordpress development workflow. Author: Atinder Singh Author URI: http://tutsplus.com Version: 1.4.1 License: GNU General Public License v2 or later License URI: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html */
Now activate this theme from the WordPress dashboard. You have your basic environment set up and ready to rock. Run gulp in terminal, and view the activated theme in your browser. Click on the live reload extension so that the live reload server gets connected, and listen to the changes.
Whenever you change any file's content in css/src or js/src, gulp will be monitoring and compiling the files and reloading your browser.
Slightly Advanced Stuff
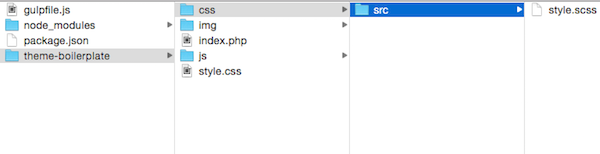
Now you have a tool that can be used for creating multiple themes, so let's move the theme files to another folder in the wp-content/themes/wp-gulp-automation/theme-boilerplate directory.
Copy the index.php and style.css files and the css, img and js folders to theme-boilerplate.
This is a very basic theme-boilerplate. You may extend this or use the one you like.
For this last task you will need three Node.js modules. Install json-file, node-fs and fs-extra.
npm install json-file --save-dev npm install node-fs --save-dev npm install fs-extra --save-dev
Require them at the top of your gulpfile.
var fs = require('node-fs');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var json = require('json-file');
var themeName = json.read('./package.json').get('themeName');
var themeDir = '../' + themeName;
Add this task to your gulpfile.
gulp.task('init', function() {
fs.mkdirSync(themeDir, 765, true);
fse.copySync('theme-boilerplate', themeDir + '/');
});
What you can do now is create a new theme in wp-content/themes using the boilerplate code like so, specifying the themeName attribute in package.json.
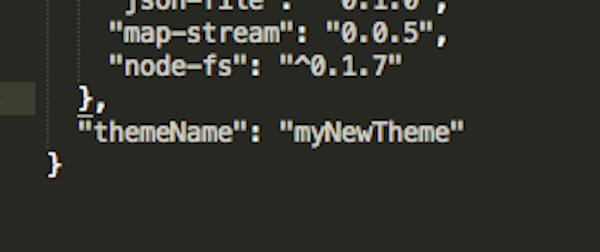
And running:
gulp init
Now you have two folders:
- wp-gulp-automation (the tool for all your themes)
- myNewTheme (your newly created theme)
.png)
The possibilities for this are endless.
You may use CoffeeScript instead of regular JavaScript and tell gulp to watch for it too. You may add more tasks depending on your workflow. Some new task ideas could be:
- removing .DS_Store, .thumb files or any unwanted files automatically
- packaging the theme into a zip folder for submission on Themeforest
Thanks for reading! If you have something to add or you have created new tasks that you can share with readers, you are welcome.


Comments