Over the course of this tutorial, we’ll review how to create an RSS Feed with the ASP.NET framework. Having an RSS feed for your site has become a necessity in recent years. With blogs or news sites being updated frequently, and with the vast amount of blogs and news websites out there, RSS has allowed readers to keep up with new content without being forced to visit them. Once you've completed this tutorial, you'll know how to create an RSS feed with ASP.NET, and how to render XML documents on ASP.NET Web pages.
Step 0: RSS 2.0 Introduction
RSS is a web content syndication format. It stands for "Really Simple Syndication," and is written in XML. All RSS files must conform to the XML 1.0 specification, as published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). With RSS, it is possible to distribute up-to-date web content from one web site to thousands of others around the world. To simplify the term, RSS allows fast browsing for news and updates.
The syntax rules of RSS 2.0 are quite simple, though strict. Here is a simple RSS document:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<rss version="2.0">
<channel>
<title>Your Website Name</title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com</link>
<description>Free RSS Tutorial</description>
<item>
<title>First Article</title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com/article.aspx?ID=1</link>
<description>The description of the first article.</description>
</item>
<item>
<title>Second Article</title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com/article.aspx?ID=2</link>
<description>The description of the second article.</description>
</item>
</channel>
</rss>
The first line in the document - the XML declaration - defines the XML version and the character encoding used in the document. In this case, the document conforms to the 1.0 specification of XML, and uses the utf-8 character set. The next line is the RSS declaration, which identifies that this is, in fact, an RSS document (more specifically, RSS version 2.0).
The next line contains the <channel> element. This element is used to describe the RSS feed. The <channel> element has three required child elements:
-
<title>- Defines the title of the channel (e.g. Your Website name) -
<link>- Defines the hyperlink to the channel (e.g. http://www.yourdomain.com) -
<description>- Describes the channel (e.g. Free RSS Tutorial)
Each <channel> element can have one or more <item> elements. Each <item> element defines an article or "story" within the RSS feed.
The <item> element requires three child elements:
-
<title>- Defines the title of the item (e.g. First Article) -
<link>- Defines the hyperlink to the item (e.g. http://www.yourdomain.com/article.aspx?ID=1) -
<description>- Describes the item (e.g. The description of the first article)
When viewed in Firefox, the RSS document above should look similar to:
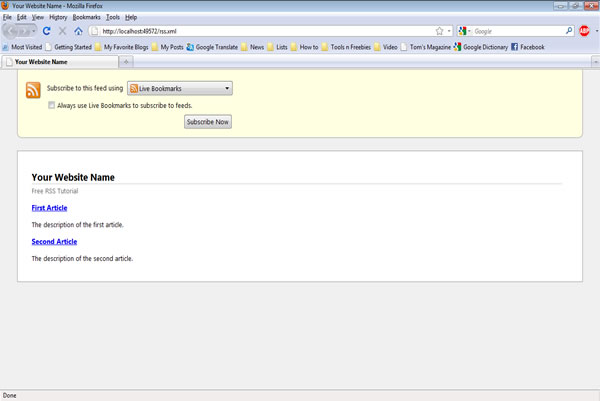
Step 1: Getting Started
To follow this tutorial, imagine that you work as a web developer, and are building a news website where all of the news stories are stored in Microsoft's SQL Server database. Specifically, the articles are stored in a table called News, which contains the following fields:
- ArticleID - an auto-increment primary key integer field uniquely identifying each article
-
Title - a
nvarchar(256), specifying the title of the article -
Author - a n
varchar(50), specifying the author of the article -
Description - a n
varchar(500), providing a more in-depth description of the article -
DatePublished - a
datetime, indicating the date the article was published
Note that there might be other fields in the News table, but those listed above are the only ones we are interested in using -- at least for the purposes of an RSS feed.
We'll use Visual Studio to finish the example. If you don’t have the full version of VS, you can grab the free Express Edition.
Step 2: Creating an rss.aspx Page
Our next step is to create an ASP.NET Web page (rss.aspx) that will display a list of the most recent news items as a properly formatted RSS 2.0 document. In Solution Explorer, right-click the project name, and then click Add New Item. In thia dialog box, under Visual Studio installed templates, click Web Form.
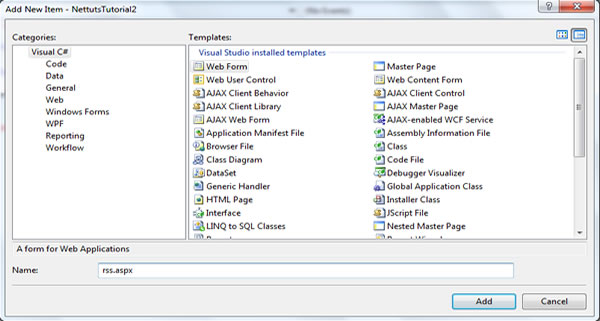
In the Name box, type a name for the new Web page (rss.aspx), and then click Add. The new ASP.NET web page (rss.aspx) is created and displayed, accordingly.
Because we want the rss.aspx page to produce XML output, the first thing that we must do is remove all HTML markup or web controls from the page, and then set the ContentType property of @page directive to "text/xml".
After clearing all HTML markup from rss.aspx page, add a Repeater control into the page. We'll use Repeater control to render RSS document on rss.aspx page.
Here is the source view of the rss.aspx page, after we've made some changes:
<%@ Page Language="C#" ContentType="text/xml" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="rss.aspx.cs" Inherits="NettutsTutorial2.rss" %> <asp:Repeater ID="RepeaterRSS" runat="server"> </asp:Repeater>
Step 3: Setup The Connection String
Next, we want to setup the connection string of the data source, within the Web.config file. By saving the connection string information, we'll avoid having to hard-code it in the code-behind file. This simplifies things, if the connection string information changes in the future. Place it in the <connectionStrings> section under configuration element, like so:
<connectionStrings> <add name="ConnectionString" connectionString="Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\Nettuts.mdf;Integrated Security=True;User Instance=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings>
We will access this information from the code-behind file later when we want to retrieve data from database.
Step 4: Removing Illegal Characters from the XML Document
Some characters have special meaning in XML. If you place a character, such as "<", inside an XML element, it will generate an error, because the parser interprets it as the start of a new element. To avoid this error, replace the "<" character with its entity reference (<).
There are five predefined entity references in XML:
| < | < | less than |
| > | > | greater than |
| & | & | ampersand |
| ' | ' | apostrophe |
| " | " | quotation mark |
To avoid our RSS feed producing an error, we have to change all illegal characters in an RSS document with their entity references. Add the following code into the code-behind file of the rss.aspx page (rss.aspx.cs):
protected string RemoveIllegalCharacters(object input)
{
// cast the input to a string
string data = input.ToString();
// replace illegal characters in XML documents with their entity references
data = data.Replace("&", "&");
data = data.Replace("\"", """);
data = data.Replace("'", "'");
data = data.Replace("<", "<");
data = data.Replace(">", ">");
return data;
}
The RemoveIllegalCharacters() function performs a few simple string replacements, if needed. We will call this function from the rss.aspx page shortly.
Step 5: Retrieving Data from the Database
Add the following code into the Page_Load event handler:
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Get connection string from the web.config file
string connString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["ConnectionString"].ConnectionString;
// Create SqlConnection object
SqlConnection sqlConn = new SqlConnection();
sqlConn.ConnectionString = connString;
// SQL query to retrieve data from database
string sqlQuery = "SELECT TOP 10 ArticleID, Title, Author, Description, DatePublished FROM News ORDER BY DatePublished DESC";
// Create SqlCommand object
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
cmd.Connection = sqlConn;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
cmd.CommandText = sqlQuery;
// open connection and then binding data into RepeaterRSS control
sqlConn.Open();
RepeaterRSS.DataSource = cmd.ExecuteReader();
RepeaterRSS.DataBind();
sqlConn.Close();
}
The code above will attempt to retrieve the ten most recent news items from your database. It will then bind them to a Repeater control (RepeaterRSS) when the page is loaded.
Step 6: Rendering Data
This is our last step. It's time to render items from the News table into an appropriate RSS 2.0 syndication file. The simplest and quickest way to display the database data as XML is to use a Repeater control (RepeaterRSS). Specifically, the Repeater will display the <rss>, <channel>, and Web site related element tags in its HeaderTemplate and FooterTemplate templates, and the <item> elements in the ItemTemplate template. Don't forget to call the helper RemoveIllegalCharacters() function to replace unwanted characters from the string output.
The following is the HTML portion of our ASP.NET Web page (rss.aspx):
<%@ Page Language="C#" ContentType="text/xml" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="rss.aspx.cs" Inherits="NettutsTutorial2.rss" %>
<asp:Repeater ID="RepeaterRSS" runat="server">
<HeaderTemplate>
<rss version="2.0">
<channel>
<title>Name of the Website</title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com</link>
<description>
Short description of the website.
</description>
</HeaderTemplate>
<ItemTemplate>
<item>
<title><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Title")) %></title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com/news.aspx?ID=<%# DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "ArticleID") %></link>
<author><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Author"))%></author>
<pubDate><%# String.Format("{0:R}", DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "DatePublished"))%></pubDate>
<description><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Description"))%></description>
</item>
</ItemTemplate>
<FooterTemplate>
</channel>
</rss>
</FooterTemplate>
</asp:Repeater>
The first thing worth noting here is that the rss.aspx file above contains only the Repeater control (RepeaterRSS), and no other HTML markup or Web controls. This is because we want the page to emit nothing but XML output. We set the ContentType of the @Page directive to "text/xml" to indicate that the output of the rss.aspx page is an XML document.
In the HeaderTemplate template of the Repeater control, we place the <rss> and <channel> elements.
Next, in the ItemTemplate, we place the <item> elements, which contain the <title>, <link>, <author>, <pubDate>, and <description> elements, as the place for database fields. We call the RemoveIllegalCharacters() function when adding the Title, Author, and Description database fields to the XML output. Remember, this function simply replaces any illegal XML characters with their entity references.
Finally, the DatePublished database field, entered into the <pubDate> element, is formatted using the String.Format method. The standard format specifier, R, formats the DatePublished value appropriately according to RFC 822, Date and Time Specification. This starts with an optional three-letter day abbreviation and comma, followed by a required day, the three-letter abbreviated month, and then the year, followed by a time with the time-zone name, such as Thu, 04 Nov 2010 20:50:26 GMT.
The Result
And there we have it! With minimal effort, we've created a custom RSS feed for an ASP.NET application.
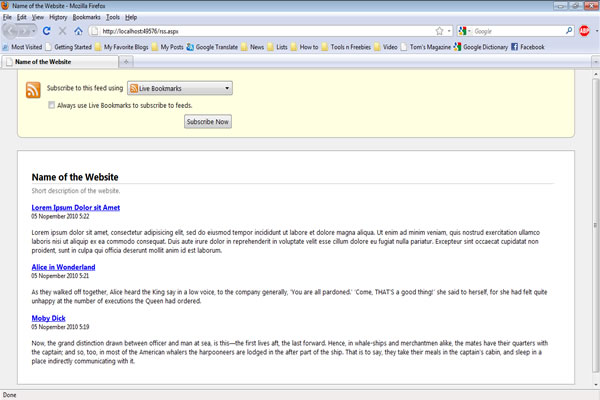
The Complete Code
The rss.aspx File
<%@ Page Language="C#" ContentType="text/xml" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="rss.aspx.cs" Inherits="NettutsTutorial2.rss" %>
<asp:Repeater ID="RepeaterRSS" runat="server">
<HeaderTemplate>
<rss version="2.0">
<channel>
<title>Name of the Website</title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com</link>
<description>
Short description of the website.
</description>
</HeaderTemplate>
<ItemTemplate>
<item>
<title><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Title")) %></title>
<link>http://www.yourdomain.com/news.aspx?ID=<%# DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "ArticleID") %></link>
<author><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Author"))%></author>
<pubDate><%# String.Format("{0:R}", DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "DatePublished"))%></pubDate>
<description><%# RemoveIllegalCharacters(DataBinder.Eval(Container.DataItem, "Description"))%></description>
</item>
</ItemTemplate>
<FooterTemplate>
</channel>
</rss>
</FooterTemplate>
</asp:Repeater>
The rss.aspx.cs File
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace NettutsTutorial2
{
public partial class rss : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Get connection string from web.config file
string connString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["ConnectionString"].ConnectionString;
// Create SqlConnection object
SqlConnection sqlConn = new SqlConnection();
sqlConn.ConnectionString = connString;
// SQL query to retrieve data from database
string sqlQuery = "SELECT TOP 10 ArticleID, Title, Author, Description, DatePublished FROM News ORDER BY DatePublished DESC";
// Create SqlCommand object
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
cmd.Connection = sqlConn;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
cmd.CommandText = sqlQuery;
// open connection and then binding data into RepeaterRSS control
sqlConn.Open();
RepeaterRSS.DataSource = cmd.ExecuteReader();
RepeaterRSS.DataBind();
sqlConn.Close();
}
protected string RemoveIllegalCharacters(object input)
{
// cast the input to a string
string data = input.ToString();
// replace illegal characters in XML documents with their entity references
data = data.Replace("&", "&");
data = data.Replace("\"", """);
data = data.Replace("'", "'");
data = data.Replace("<", "<");
data = data.Replace(">", ">");
return data;
}
}
}
The Web.config File
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<sectionGroup name="system.web.extensions" type="System.Web.Configuration.SystemWebExtensionsSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35">
<sectionGroup name="scripting" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35">
<section name="scriptResourceHandler" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingScriptResourceHandlerSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission="false" allowDefinition="MachineToApplication"/>
<sectionGroup name="webServices" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingWebServicesSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35">
<section name="jsonSerialization" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingJsonSerializationSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission="false" allowDefinition="Everywhere"/>
<section name="profileService" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingProfileServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission="false" allowDefinition="MachineToApplication"/>
<section name="authenticationService" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingAuthenticationServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission="false" allowDefinition="MachineToApplication"/>
<section name="roleService" type="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingRoleServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission="false" allowDefinition="MachineToApplication"/>
</sectionGroup>
</sectionGroup>
</sectionGroup>
</configSections>
<appSettings/>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="ConnectionString" connectionString="Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\Nettuts.mdf;Integrated Security=True;User Instance=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient"/>
</connectionStrings>
<system.web>
<!--
Set compilation debug="true" to insert debugging
symbols into the compiled page. Because this
affects performance, set this value to true only
during development.
-->
<compilation debug="true">
<assemblies>
<add assembly="System.Core, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089"/>
<add assembly="System.Data.DataSetExtensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089"/>
<add assembly="System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add assembly="System.Xml.Linq, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089"/>
</assemblies>
</compilation>
<!--
The <authentication> section enables configuration
of the security authentication mode used by
ASP.NET to identify an incoming user.
-->
<authentication mode="Windows"/>
<!--
The <customErrors> section enables configuration
of what to do if/when an unhandled error occurs
during the execution of a request. Specifically,
it enables developers to configure html error pages
to be displayed in place of a error stack trace.
<customErrors mode="RemoteOnly" defaultRedirect="GenericErrorPage.htm">
<error statusCode="403" redirect="NoAccess.htm" />
<error statusCode="404" redirect="FileNotFound.htm" />
</customErrors>
-->
<pages>
<controls>
<add tagPrefix="asp" namespace="System.Web.UI" assembly="System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add tagPrefix="asp" namespace="System.Web.UI.WebControls" assembly="System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
</controls>
</pages>
<httpHandlers>
<remove verb="*" path="*.asmx"/>
<add verb="*" path="*.asmx" validate="false" type="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add verb="*" path="*_AppService.axd" validate="false" type="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add verb="GET,HEAD" path="ScriptResource.axd" type="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptResourceHandler, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" validate="false"/>
</httpHandlers>
<httpModules>
<add name="ScriptModule" type="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
</httpModules>
</system.web>
<system.codedom>
<compilers>
<compiler language="c#;cs;csharp" extension=".cs" warningLevel="4" type="Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider, System, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089">
<providerOption name="CompilerVersion" value="v3.5"/>
<providerOption name="WarnAsError" value="false"/>
</compiler>
</compilers>
</system.codedom>
<!--
The system.webServer section is required for running ASP.NET AJAX under Internet
Information Services 7.0. It is not necessary for previous version of IIS.
-->
<system.webServer>
<validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration="false"/>
<modules>
<remove name="ScriptModule"/>
<add name="ScriptModule" preCondition="managedHandler" type="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
</modules>
<handlers>
<remove name="WebServiceHandlerFactory-Integrated"/>
<remove name="ScriptHandlerFactory"/>
<remove name="ScriptHandlerFactoryAppServices"/>
<remove name="ScriptResource"/>
<add name="ScriptHandlerFactory" verb="*" path="*.asmx" preCondition="integratedMode" type="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add name="ScriptHandlerFactoryAppServices" verb="*" path="*_AppService.axd" preCondition="integratedMode" type="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
<add name="ScriptResource" preCondition="integratedMode" verb="GET,HEAD" path="ScriptResource.axd" type="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptResourceHandler, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35"/>
</handlers>
</system.webServer>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Extensions" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35"/>
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.1.0.0" newVersion="3.5.0.0"/>
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Extensions.Design" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35"/>
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.1.0.0" newVersion="3.5.0.0"/>
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>
Conclusion
Creating an RSS feed with ASP.NET is quite simple, isn't it? We only need to understand the RSS 2.0 specification. Beyond that, by using the .NET Repeater control, we can render items from a database into the RSS document. Most content management systems will have this capability by default. However, if you're a developer, and are building an ASP.NET website from scratch, you now have the skills to build your own custom feed.
Happy Coding!


Comments