At work we previously used KBPublisher to manage our knowledge base. It costed money, it was hard to style, code is encrypted with ion cube and so on, basically very hard to maintain. WordPress can do the same things and even better.
This tutorial will show you how to use custom taxonomies for knowledge base sections and custom posts for knowledge base articles.
Step 1 Administration
Knowledge base sections and articles need to be managed. WordPress makes this easy to do with custom taxonomies and custom post types.
Just register the new taxonomy and post type. Add the following into functions.php from your theme.
For more information on the ins and outs of this functionality, read our other custom post type and custom taxonomy articles.
function register_kb() {
register_post_type( 'knowledgebase',
array(
'labels' => array(
'name' => 'Knowledge Base',
'menu_name' => 'Knowledge Base',
'singular_name' => 'Article',
'all_items' => 'All Articles'
),
'public' => true,
'publicly_queryable' => true,
'show_ui' => true,
'show_in_menu' => true,
'show_in_nav_menus' => true,
'menu_position ' => 20,
'supports' => array( 'title', 'editor', 'author', 'thumbnail', 'comments', 'post-formats', 'revisions' ),
'hierarchical' => false,
'taxonomies' => array( 'section' ),
'has_archive' => true,
'rewrite' => array( 'slug' => 'knowledgebase', 'hierarchical' => true, 'with_front' => false )
)
);
register_taxonomy( 'section', array( 'knowledgebase' ),
array(
'labels' => array(
'name' => 'Sections',
'menu_name' => 'Sections',
'singular_name' => 'Section',
'all_items' => 'All Sections'
),
'public' => true,
'hierarchical' => true,
'show_ui' => true,
'rewrite' => array( 'slug' => 'knowledgebase-section', 'hierarchical' => true, 'with_front' => false ),
)
);
}
add_action( 'init', 'register_kb' );
function kb_rewrite_rules( $wp_rewrite ) {
$new_rules = array( 'knowledgebase/(.*)/(.*)' => 'index.php?post_type=knowledgebase§ion=' . $wp_rewrite->preg_index( 1 ) . '&knowledgebase=' . $wp_rewrite->preg_index( 2 ) );
$wp_rewrite->rules = $new_rules + $wp_rewrite->rules;
}
add_action( 'generate_rewrite_rules', 'kb_rewrite_rules' );
This will run after WordPress has finished loading but before any headers are sent, registering the post type and taxonomy. Also, it will add the rewrite rules for the permalinks of the taxonomy and post type.
The register_post_type registers the custom post type, this is used for the KB articles. The register_taxonomy registers the custom taxonomy, this is used for the KB sections. The articles won't be hierarchical but the sections will be, so it gives the possibility to create a tree structure.
Also it would be nice to show the sections that an article is assigned to.
function kb_columns( $defaults ) {
$defaults['section'] = 'Sections';
return $defaults;
}
add_filter( 'manage_knowledgebase_posts_columns', 'kb_columns' );
function kb_custom_column( $column_name, $post_id ) {
$taxonomy = $column_name;
$post_type = get_post_type( $post_id );
$terms = get_the_terms( $post_id, $taxonomy );
if ( !empty( $terms ) ) {
foreach ( $terms as $term ) {
$post_terms[] = "<a href='edit.php?post_type={$post_type}&{$taxonomy}={$term->slug}'> " . esc_html(sanitize_term_field('name', $term->name, $term->term_id, $taxonomy, 'edit')) . '</a>';
}
echo join( ', ', $post_terms );
}
else echo '<i>No terms.</i>';
}
add_action( 'manage_knowledgebase_posts_custom_column', 'kb_custom_column', 10, 2 );
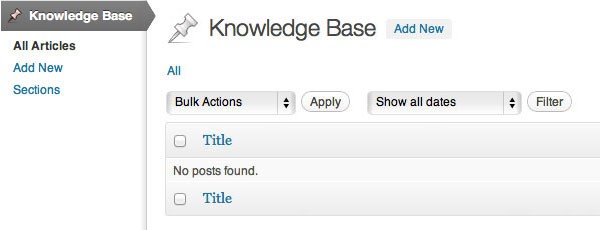
Now add some sections and some articles so there is something to show.
Step 2 Showing the Sections
Add the following into functions.php from your theme.
function kb_sections( $sections = array(), $active_section = null ) {
$taxonomy = 'section';
$link_class = '';
if ( empty( $sections ) ) {
$link_class = 'root';
$sections = get_terms( $taxonomy, array( 'parent' => 0, 'hide_empty' => 0 ) );
$active_section = kb_active_section();
echo '<ul id="kb-sections" class="unstyled">';
}
if ( empty( $active_section ) ) {
$active_section = '';
}
foreach ( $sections as $section ) {
$toggle = '';
$section_children = get_terms( $taxonomy, array( 'parent' => $section->term_id, 'hide_empty' => 0 ) );
if ( !empty( $section_children ) && $link_class != 'root' ) {
$toggle = '<i class="toggle"></i>';
}
echo '<li class="' . ( $section->term_id == $active_section ? 'active' : '' ) . '">';
echo '<a href="' . get_term_link( $section, $taxonomy ) . '" class="' . $link_class . '" rel="' . $section->slug . '">' . $toggle . $section->name . '</a>';
if ( !empty( $section_children ) ) {
echo '<ul id="' . $section->slug . '" class="children">';
kb_sections( $section_children, $active_section );
}
echo "</li>";
}
echo "</ul>";
}
function kb_active_section() {
$taxonomy = 'section';
$current_section = '';
if ( is_single() ) {
$sections = explode( '/', get_query_var( $taxonomy ) );
$section_slug = end( $sections );
if ( $section_slug != '' ) {
$term = get_term_by( 'slug', $section_slug, $taxonomy );
} else {
$terms = wp_get_post_terms( get_the_ID(), $taxonomy );
$term = $terms[0];
}
$current_section = $term->term_id;
} else {
$term = get_term_by( 'slug', get_query_var( $taxonomy ), get_query_var( 'taxonomy' ) );
$current_section = $term->term_id;
}
return $current_section;
}
In the theme folder create a file called sidebar-sections.php where your kb_sections function will be called outputting an unordered and nested list of sections.
<?php kb_sections(); ?>
Like this, the KB sections can be shown everywhere as desired by including the sidebar.
<?php get_sidebar( 'sections' ); ?>
Step 3 Showing the Articles
Add the following into functions.php from your theme.
function kb_article_permalink( $article_id, $section_id ) {
$taxonomy = 'section';
$article = get_post( $article_id );
$section = get_term( $section_id, $taxonomy );
$section_ancestors = get_ancestors( $section->term_id, $taxonomy );
krsort( $section_ancestors );
$permalink = '<a href="/knowledgebase/';
foreach ($section_ancestors as $ancestor):
$section_ancestor = get_term( $ancestor, $taxonomy );
$permalink.= $section_ancestor->slug . '/';
endforeach;
$permalink.= $section->slug . '/' . $article->post_name . '/" >' . $article->post_title . '</a>';
return $permalink;
}
Note: this method is necessary because an article can be linked to multiple sections.
This will generate a hierarchical permalink structure.
Like: /knowledgebase/section-slug/sub-section-slug/another-sub-section-slug/article-slug
In the theme folder then create these files: archive-knowledgebase.php, single-knowledgebase.php, content-knowledgebase.php, taxonomy-section.php.
In archive-knowledgebase.php add the following to show the sections and recent articles.
<?php get_header(); get_sidebar( 'sections' ); while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); $terms = wp_get_post_terms( $post->ID, 'section' ); $term = $terms[0]; echo kb_article_permalink( $post->ID, $term->term_id ); endwhile; get_footer(); ?>
In single-knowledgebase.php add the following.
<?php get_header(); while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); get_template_part( 'content', 'knowledgebase' ); endwhile; get_footer(); ?>
In content-knowledgebase.php add the following.
<?php get_sidebar( 'sections' ); the_title(); the_content(); ?>
In taxonomy-section.php add the following to show a list of articles from a section.
<?php global $wp_query; $args = array_merge( $wp_query->query, array( 'posts_per_page' => 100 ) ); query_posts( $args ); $term = get_term_by( 'slug', get_query_var( 'term' ), 'section' ); get_header(); get_sidebar( 'sections' ); while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); echo kb_article_permalink( $post->ID, $term->term_id ); endwhile; get_footer(); ?>
This can be structured and styled as desired.
Example
A real life example of how this works and how it can be used: syneto.net


Comments