When it comes to design patterns, you may have questions:
Why should we use design patterns in programming? Our code can work just fine without it.
To that, my counter question would be: "Would you rather live in a luxurious home, or in a simple establishment with four walls?" After all, both serve our purpose.
Generally, we look for a luxurious home because it offers better facilities and requires less maintenance, and maintenance can done with less hassle because the basic groundwork is already there.
The same thing applies to programming: Code that employs design patterns is easy to understand, easy to maintain, and easy to extend.
In this series of tutorials, we will cover some different design patterns that are available to us in programming. You'll learn about their pros and cons, and factors that indicate where we should use them.
Throughout these tutorials, I will take PHP as a base language to demonstrate design patterns; however, they are actually a concept that can be applied to any programming language—it's just a matter of changing the syntax as per your preferred language.
Design rules are separated into four categories:
- creational patterns
- structural patterns
- behavioral patterns
- concurrency patterns
In this tutorial, we are going to cover the facade design pattern. It falls under the category of structural patterns because it deals with how your code should be structured to make it easily intelligible and keep it well maintained in the long term.
Facade Design Pattern
The UML
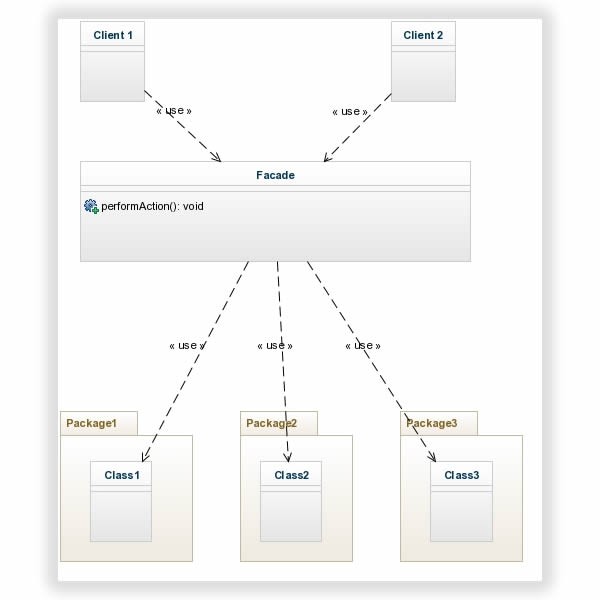
Problem
Let's assume that you have a few operations to be made in sequence, and that the same action is required in multiple places within your application. You have to place the same code again and again in different places. You have done that, but after a few days you find that something needs to be changed in that code.
Do you see the problem? We have to introduce the changes in all of the places that the code exists. It's painful, isn't it?
Solution
As a solution, what you should be doing is to create a lead controller, which handles all of the repeating code. From the calling point of view, we will just call the lead controller to perform actions based on the parameters provided.
Now if we need to introduce any change in the process, then we will just need to change the lead controller instead of making the change in all places where we used that code.
Example
In this tutorial, let's choose one lesson so that it makes things more readable. Let's say that you have been given a task to plan your friend's marriage. If you do everything on your own, then imagine the things you need to cover. It will create a higher possibility for error, and increase the chance of missing something that can drastically affect your friend's wedding.
In this case, instead of doing everything on your own, you should use a wedding planner and make sure the job gets done in a well-managed manner with less chance of a mistake.
Here, you are behaving as a client who initiates the process, and the wedding planner is working as a "facade" for you, completing the job based on your direction.
Code Example
In this section we will see one more example, which is very common for websites, of course with a code example. We will see an implementation of the facade design pattern using a product checkout process. But before checking perfect code with the facade pattern, let's have a look at some code that has a problem.
A simple checkout process includes the following steps:
- Add product to cart.
- Calculate shipping charge.
- Calculate discount.
- Generate order.
Problem
// Simple CheckOut Process
$productID = $_GET['productId'];
$qtyCheck = new productQty();
if($qtyCheck->checkQty($productID) > 0) {
// Add Product to Cart
$addToCart = new addToCart($productID);
// Calculate Shipping Charge
$shipping = new shippingCharge();
$shipping->updateCharge();
// Calculate Discount Based on
$discount = new discount();
$discount->applyDiscount();
$order = new order();
$order->generateOrder();
}
In the above code, you will find that the checkout procedure includes various objects that need to be produced in order to complete the checkout operation. Imagine that you have to implement this process in multiple places. If that's the case, it will be problematic when the code needs to be modified. It's better to make those changes in all places at once.
Solution
We will write the same thing with the facade pattern, which makes the same code more maintainable and extendable.
class productOrderFacade {
public $productID = '';
public function __construct($pID) {
$this->productID = $pID;
}
public function generateOrder() {
if($this->qtyCheck()) {
// Add Product to Cart
$this->addToCart();
// Calculate Shipping Charge
$this->calulateShipping();
// Calculate Discount if any
$this->applyDiscount();
// Place and confirm Order
$this->placeOrder();
}
}
private function addToCart () {
/* .. add product to cart .. */
}
private function qtyCheck() {
$qty = 'get product quantity from database';
if($qty > 0) {
return true;
} else {
return true;
}
}
private function calulateShipping() {
$shipping = new shippingCharge();
$shipping->calculateCharge();
}
private function applyDiscount() {
$discount = new discount();
$discount->applyDiscount();
}
private function placeOrder() {
$order = new order();
$order->generateOrder();
}
}
As of now, we have our product order facade ready. All we have to do is use it with a few communication channels of code, instead of a bunch of code as expressed in the previous part.
Please check the amount of code below which you will need to invest in order to have a checkout process at multiple positions.
// Note: We should not use direct get values for Database queries to prevent SQL injection $productID = $_GET['productId']; // Just 2 lines of code in all places, instead of a lengthy process everywhere $order = new productOrderFacade($productID); $order->generateOrder();
Now imagine when you need to make alterations in your checkout process. Now you simply create changes in the facade class that we have created, rather than introducing changes in every place where it has been applied.
Conclusion
Simply put, we can say that the facade pattern should be carried out in a situation where you need a single interface to complete multiple procedures, as in the example of the wedding planner who is working as a facade for you to complete multiple procedures.
Please leave any comments or questions in the feed below.


Comments