In the previous part of this tutorial series, we created a custom directive and used it in our simple shopping cart application. In this part of the tutorial series, we'll see how to make the total div stick to the top while scrolling the browser. We'll also create a checkout page where we'll display all the items selected by the user.
Getting Started
Let's start by cloning the previous part of the tutorial from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/jay3dec/AngularShoppingCart_Part2.git
After cloning the source code, navigate to the project directory and install the required dependencies.
cd AngularShoppingCart_Part2 npm install
Once the dependencies are installed, start the server
node server.js
Point your browser to http://localhost:3000/ and you should have the application running.
Affix the Total Div
Although we are using the bootstrap affix component to keep the total div on the top, it isn't working as expected. Let's examine what's going wrong.
The bootstrap affix component adds a class called affix when we scroll above a certain height and affix-top when it's below. It still works in the simple HTML pages, but when integrated into AngularJS it doesn't seem to work. In order to fix this issue, we'll keep a check on the scroll height and when it's above and below a certain height, say 50 px, we'll add the affix classes accordingly.
So, assuming that we have the scroll height as scroll, add the affix and affix-top classes to the Total div using the ngClass directive.
ng-class="{'affix': scroll > 50, 'affix-top': scroll <= 50}"
In order to get the scroll we'll create another directive. Let's name the directive getScroll. This directive will update the scroll value each time the browser window is scrolled, and based on scroll the affix classes will be updated.
.directive('getScroll', function($window) {
return {
scope: {
scroll: '=scroll'
},
link: function(scope, element, attrs) {
var scrollwindow = angular.element($window);
scrollwindow.on('scroll', scope.$apply.bind(scope, function() {
scope.scroll = scrollwindow.scrollTop();
}));
}
};
})
As seen in the above code, we are passing a scroll attribute to the getScroll directive. On scroll we are calculating the scroll height from the top using angular.element($window). On each scroll event we update the scroll scope variable.
Add the above directive to the end of the cart.html page.
<get-scroll scroll="scroll"></get-scroll>
Save these changes and refresh the page. Try to scroll the browser window and the total should be affixed on the top, always visible.
Implementing a Checkout Page
To populate the checkout page with the items selected, we'll need to pass the items between controllers. So we'll make use of an AngularJS service to pass the data between controllers. Let's create a service called CommonProp where we'll save the items selected and also the total price. Open up cart.js and create a service called CommonProp as shown:
.service('CommonProp', function() {
var Items = '';
var Total = 0;
return {
getItems: function() {
return Items;
},
setItem: function(value) {
Items = value;
},
getTotal: function(){
return Total;
},
setTotal: function(value){
Total = value;
}
};
});
As seen, inside the CommonProp service we have defined four functions to get and set the items and total price. Inject the CommonProp service into the CartCtrl.
.controller('CartCtrl', ['$scope','CommonProp',function($scope,CommonProp) {
We'll watch for any change in the shopData variable and update the service data accordingly. Add the following code inside CartCtrl.
$scope.$watch('shopData',function(){
CommonProp.setItem($scope.shopData);
})
Inside checkout.js, inject the CommonProp service into CheckoutCtrl.
.controller('CheckoutCtrl', ['$scope','CommonProp',function($scope,CommonProp) {
We'll be using the CommonProp service to get the items and total in CheckoutCtrl.
.controller('CheckoutCtrl', ['$scope','CommonProp',function($scope,CommonProp) {
$scope.items = CommonProp.getItems();
$scope.total = CommonProp.getTotal();
}]);
Using $scope.items we'll populate the checkout page. Open up checkout.html and remove the existing hard-coded table. We'll make use of the ngRepeat directive and $scope.items to create the table and populate it dynamically.
<table class="table">
<tr ng-repeat="i in items">
<td>
{{i.item}}
</td>
<td>
Rs. {{i.selected}}
</td>
</tr>
</table>
Save the above changes and refresh the page. Select a few items and then click on the Checkout button in the cart page. Once on the checkout page, it should display the list of items selected.
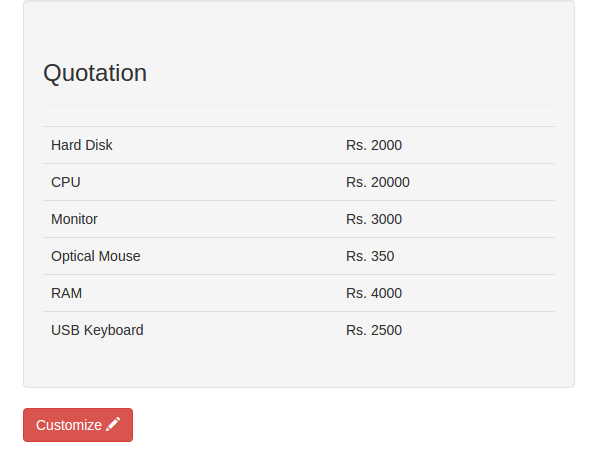
Let's also include the Price total in the checkout page. So when the total is calculated in the total function in CartCtrl, update the CommonProp service total value.
$scope.total = function() {
var t = 0;
for (var k in $scope.shopData) {
t += parseInt($scope.shopData[k].selected);
}
CommonProp.setTotal(t);
return t;
}
To display the total on the checkout page, include the following tr HTML code:
<tr>
<td>
<b>Total:</b>
</td>
<td>
<b>Rs. {{total}}</b>
</td>
</tr>
Since we are updating the total scope variable in CheckoutCtrl, the total will automatically be displayed. Save the changes and start afresh. Select a few items and select checkout. Once on the checkout page you should be able to see the selected items and the total price.

Once on the checkout page, if you click the Customize button you'll be taken to the cart page, but all the selections will be gone. So we need to fix that. Once the cart page is loaded, we'll check the CommonProp service for any existing items. If items are present then we'll use those items to populate the cart page.
Inside CartCtrl check if any items exist in CommonProp and set the $scope.shopData.
if (CommonProp.getItems() != '') {
$scope.shopData = CommonProp.getItems();
}
Save all the above changes and restart the server. From the cart page, select a few items and then click Checkout to navigate to the checkout page. Once on the checkout page, click on the Customize button to get back to the cart page. And you should have all the selections made, as they are, in the cart page.
Conclusion
In this part of the tutorial series, we implemented the checkout page and saw how to share data between different controllers using an AngularJS service. We also created a directive to get the scroll height and fix the bootstrap affix issue.
I hope you learnt something useful from this tutorial series. For more in-depth information regarding AngularJS directives, have a look at the official documentation.
Source code from this tutorial is available on GitHub. Do let us know your thoughts and corrections in the comments below!


Comments